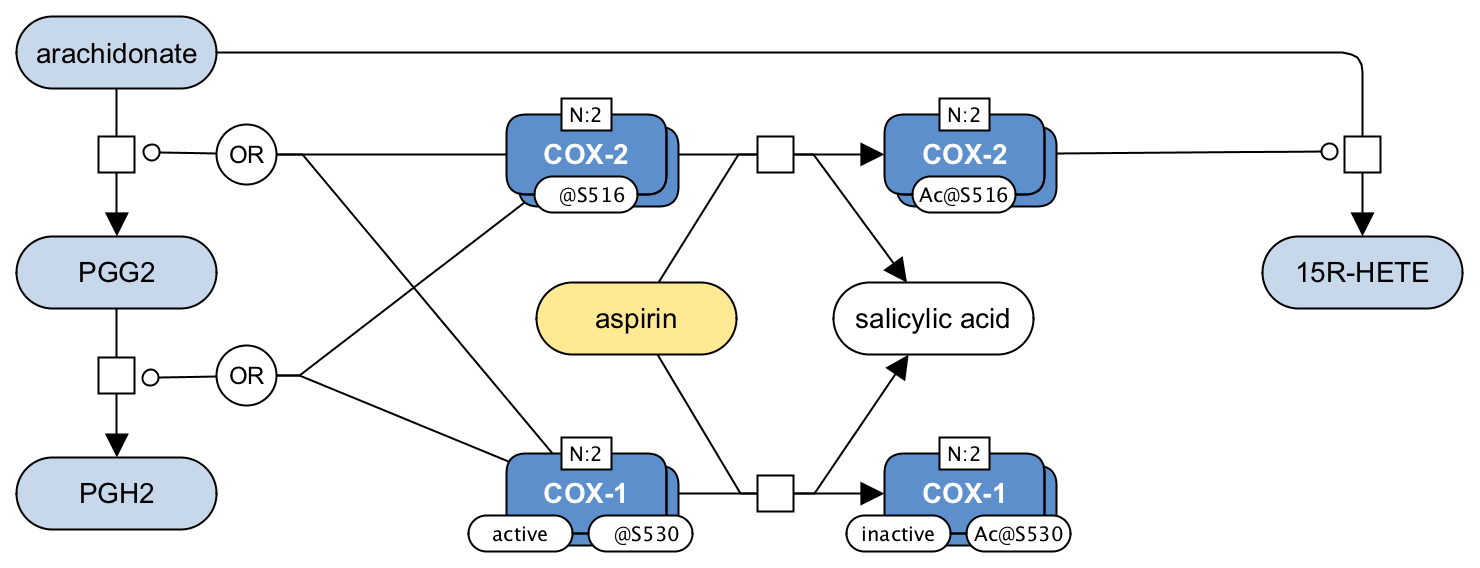
Regulation of eisocanoid metabolism by aspirin
Downloads: GraphML SBGN-ML Newt CellDesigner MINERVA
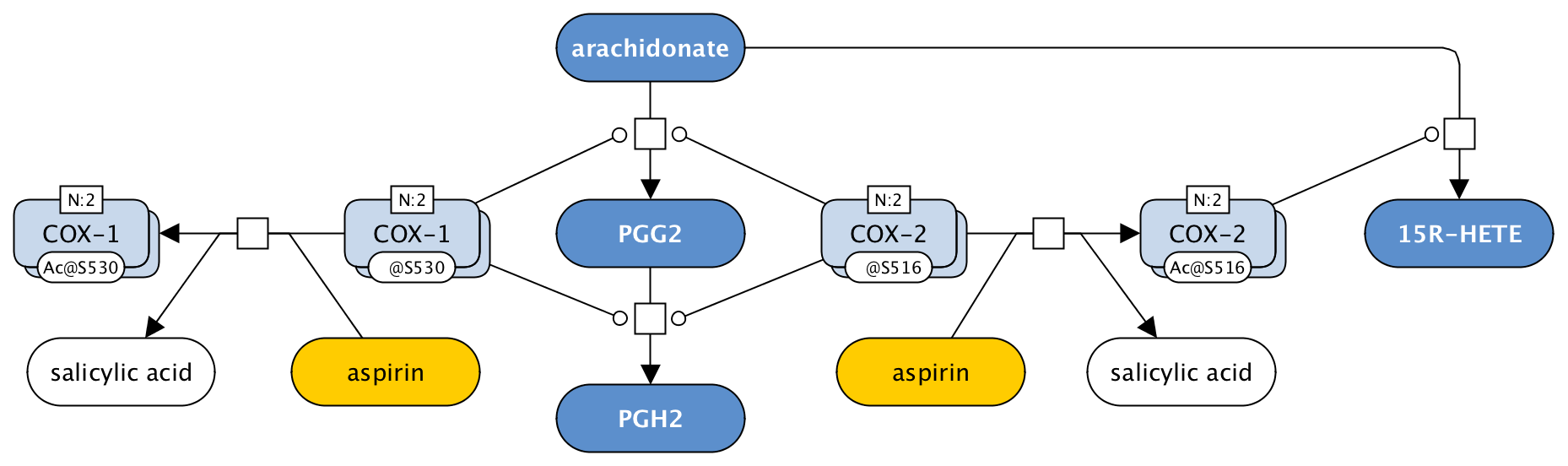
Regulation of eisocanoid metabolism by aspirin: alternative version
Downloads: GraphML SBGN-ML Newt CellDesigner MINERVA
Contributors
Alexander Mazein, Maria Heredia Chavez (annotation)
References
-
Ornelas A, Zacharias-Millward N, Menter DG, Davis JS, Lichtenberger L, Hawke D, Hawk E, Vilar E, Bhattacharya P, Millward S. Beyond COX-1: the effects of aspirin on platelet biology and potential mechanisms of chemoprevention. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017 Jun;36(2):289-303. doi: 10.1007/s10555-017-9675-z. Review. PMID: 28762014.
-
Lucido MJ, Orlando BJ, Vecchio AJ, Malkowski MG. Crystal Structure of Aspirin-Acetylated Human Cyclooxygenase-2: Insight into the Formation of Products with Reversed Stereochemistry. Biochemistry. 2016 Mar 1;55(8):1226-38. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01378. PMID: 26859324.
-
Chiang N, Bermudez EA, Ridker PM, Hurwitz S, Serhan CN. Aspirin triggers antiinflammatory 15-epi-lipoxin A4 and inhibits thromboxane in a randomized human trial. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Oct 19;101(42):15178-83. PMID: 15471991.
-
Awtry EH, Loscalzo J. Aspirin. Circulation. 2000 Mar 14;101(10):1206-18. Review. PMID: 10715270.
-
Rowlinson SW, Crews BC, Goodwin DC, Schneider C, Gierse JK, Marnett LJ. Spatial requirements for 15-(R)-hydroxy-5Z,8Z,11Z, 13E-eicosatetraenoic acid synthesis within the cyclooxygenase active site of murine COX-2. Why acetylated COX-1 does not synthesize 15-(R)-hete. J Biol Chem. 2000 Mar 3;275(9):6586-91. PMID: 10692466.