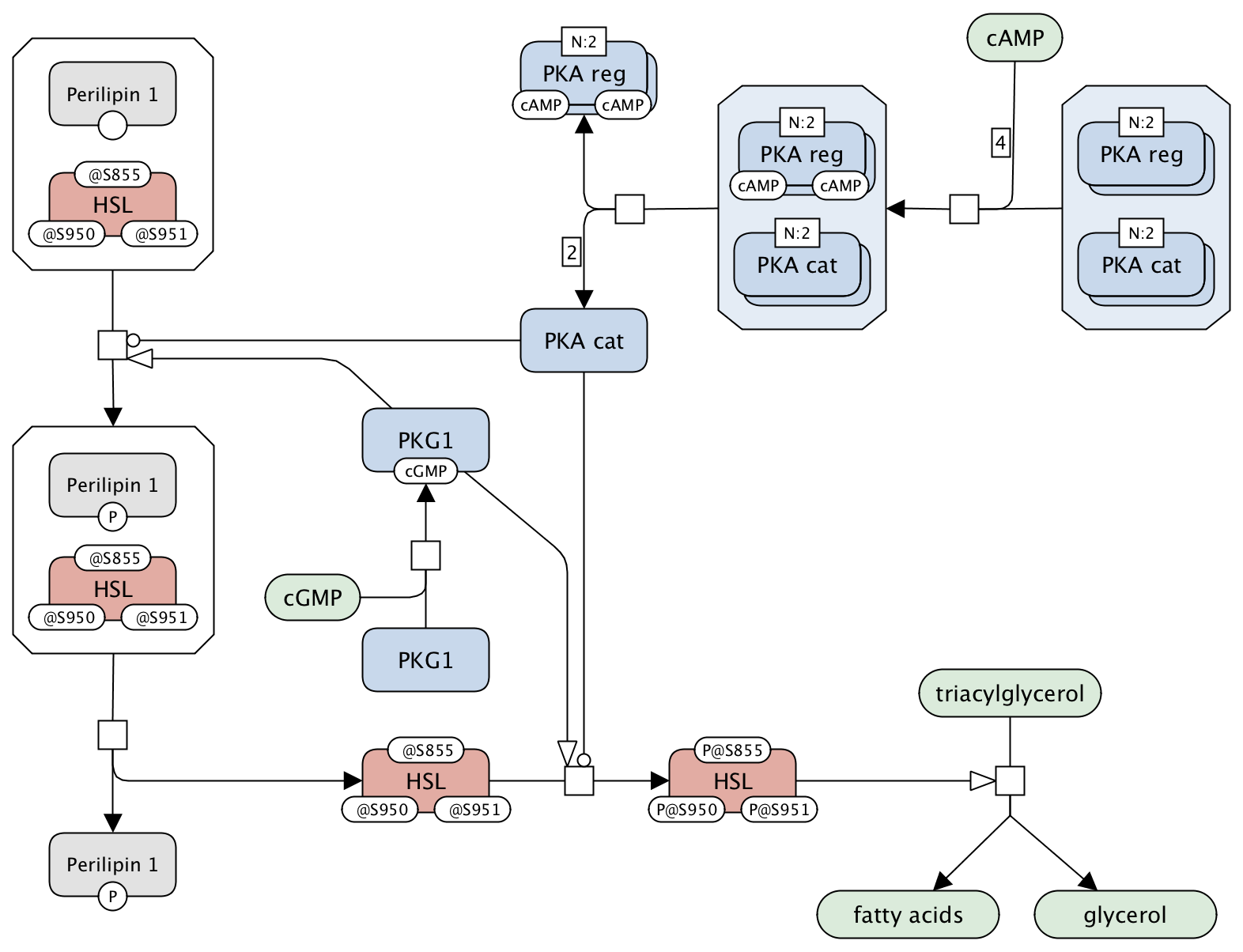
Regulation of triacylglycerol hydrolysis
Downloads: GraphML SBGN-ML CellDesigner MINERVA Newt
Contributors
Tatiana Serebriyskaya, Valeriya Berzhitskaya, John Albanese (annotation)
Description
Hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) is a major enzyme involved in triacylglycerol lipolysis, and its activity is controlled by phosphorylation in response to adrenergic and intracellular effectors in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. Lipolysis is the hydrolysis of triacylglycerol to release fatty acids and glycerol as energy substrates. Fatty acids derived from adipose tissue is an important energy source for use by other organs, such as liver, skeletal muscle, kidney and myocardium.
References
- KEGG Pathway Maps: Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes
- Database dbPTM: LIPS_HUMAN
- Duncan RE, Ahmadian M, Jaworski K, Sarkadi-Nagy E, Sul HS. Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes. Annu Rev Nutr. 2007;27:79-101 PMID: 17313320
- Carmen GY, Víctor SM. Signalling mechanisms regulating lipolysis. Cell Signal. 2006 Apr;18(4):401-8. PMID: 16182514
- Watt MJ, Holmes AG, Pinnamaneni SK, Garnham AP, Steinberg GR, Kemp BE, Febbraio MA. Regulation of HSL serine phosphorylation in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006 Mar;290(3):E500-8. PMID: 16188906
- Sengenes C, Bouloumie A, Hauner H, Berlan M, Busse R, Lafontan M, Galitzky J. Involvement of a cGMP-dependent pathway in the natriuretic peptide-mediated hormone-sensitive lipase phosphorylation in human adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 2003 Dec 5;278(49):48617-26. PMID: 12970365
- Shen WJ, Patel S, Miyoshi H, Greenberg AS, Kraemer FB. Functional interaction of hormone-sensitive lipase and perilipin in lipolysis. J Lipid Res. 2009 Nov;50(11):2306-13. PMID: 19515989
- Miyoshi H1, Perfield JW 2nd, Souza SC, Shen WJ, Zhang HH, Stancheva ZS, Kraemer FB, Obin MS, Greenberg AS.Control of adipose triglyceride lipase action by serine 517 of perilipin A globally regulates protein kinase A-stimulated lipolysis in adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 2007 Jan 12;282(2):996-1002. PMID: 17114792